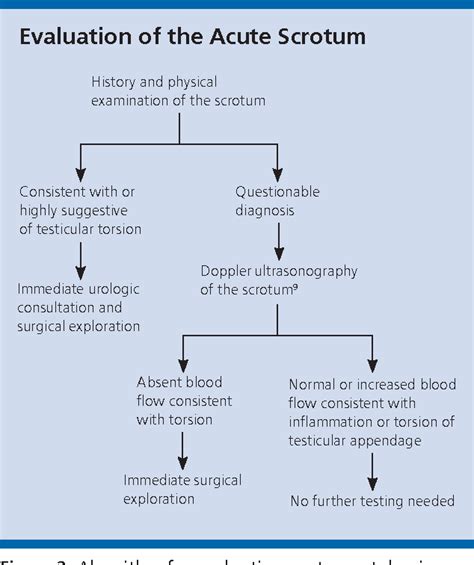
prehn's test in testicular torsion|testicular torsion after surgery : chain store A scrotal ultrasound (C) is the first-line imaging test recommended to rule in or out testicular torsion and should only be performed before surgical consult when patients with testicular pain have reassuring findings on history . Resultado da Você por dentro de tudo - Notícias ao vivo, fatos da política nacional e internacional no maior canal de notícias do mundo!
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 它支持内置硬件组件并包含相应的驱动器和控制器固件,并将 ViALUX 的 FPGA 逻辑设计用于 EVM 电路板。ALP-4.1 控制器套件支持所有使用 DLPC410 控制器的 DMD:DLP7000、DLP7000UV、DLP9500、DLP9500UV 和 DLP650LNIR。 支持的刷新率 Vialux
ultrasound testicular torsion test
Prehn's sign (named after urologist Douglas T. Prehn) is a medical diagnostic indicator that was once believed to help determine whether the presenting testicular pain is caused by acute epididymitis or from testicular torsion. Although elevation of the scrotum when differentiating epididymitis from testicular torsion is of clinical value, Prehn's sign has been shown to be inferior to Doppler ultrasound to rule out testicular torsion.Testicular torsion is a time-sensitive diagnosis that requires prompt surgical intervention to avoid testicular ischemia, infertility, and unwanted litigation. When imaging is required, the .
thickness measurement optical reflectance
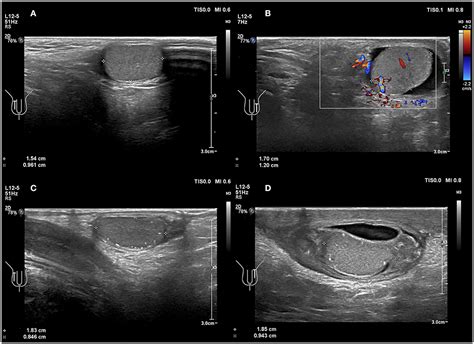
Testicular torsion is a true urologic emergency, and early identification is critical to prevent the need for testicular amputation. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to . A scrotal ultrasound (C) is the first-line imaging test recommended to rule in or out testicular torsion and should only be performed before surgical consult when patients with testicular pain have reassuring findings on history . In multivariate analysis, a positive Prehn’s sign was predictive of testicular torsion, whereas fever, dysuria, high leucocyte counts in blood and/or urine, high blood C .
Prehn's sign is used to discriminate between bacterial epididymitis and testicular torsion. Scrotal elevation relieves pain in epididymitis but not torsion. Study evidence . Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency with a 4-6hrs window from the onset of symptoms to salvage the testis before significant ischaemic damage occurs. Any suspected case warrants urgent surgical exploration of .
Epididymitis is often confused with testicular torsion, use of the Prehn's sign may be helpful, but should always be followed with imaging to confirm the diagnosis. The ultrasound of the testicle .There is usually an associated hydrocoele with scrotal wall erythema; however, these are common examination findings of many diagnoses of acute scrotal pain. 7 If elevation of the scrotum does not relieve the pain (negative Prehn’s .A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).
1 Introduction2 Clinical Features3 Investigations4 Differential Diagnosis4.1 Testicular Torsion4.2 Torsion of Testicular and Epididymal Appendages4.3 Epididymitis4.4 Testicular Cancer4.5 Referred Pain5 Non . Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18. Previous testicular torsion. If you've had testicular pain that went away without treatment (intermittent torsion and detorsion), it's likely to occur again. The more frequent the bouts of pain, the higher the risk of testicular damage. Family history of testicular torsion. An absent cremasteric reflex is suggestive of testicular torsion (odds ratio = 7.8), whereas the reflex is preserved with epididymitis. 10 – 12 Torsion of the appendix testis is classically . Prehn’s Sign. Prehn’s sign is the relief of pain with elevation of the testis commonly seen in patients with epididymitis. It does not reliably distinguish epididymitis from torsion. One cross section study of 120 patients found the Prehn’s sign was present in 91% of patients with torsion and 21% of those with epididymitis.
Epididymitis is often confused with testicular torsion, use of the Prehn's sign may be helpful, but should always be followed with imaging to confirm the diagnosis. The ultrasound of the testicle with flow Doppler is still the preferred diagnostic treatment tool after a thorough history and physical examination has been completed.B. Ultrasound evaluation with Doppler color flow Testicular torsion should be suspected in patients who complain of acute scrotal pain and swelling. Testicular viability is in jeopardy with delay in diagnosis, ultimately impacting the patient fertility. Acute scrotum pain is defined as “the constellation of new-onset pain, swelling, and/or tenderness of the intrascrotal contents.” Patients may describe the onset of symptoms as rapidly as occurring within minutes or up to 1 to 2 days, dependent on the etiology. The acute scrotum is an umbrella term that includes a wide variety of unique disease processes. Rapid . Prehn’s Sign. Prehn’s sign is the relief of pain with elevation of the testis commonly seen in patients with epididymitis. It does not reliably distinguish epididymitis from torsion. One cross section study of 120 patients found the Prehn’s sign was present in 91% of patients with torsion and 21% of those with epididymitis.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity. The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. . This presentation helps differentiate epididymitis and orchitis from testicular torsion, which is a surgical emergency. . with testicular torsion. 4, 18, 19 Prehn . results of these tests if .
In multivariate analysis, a positive Prehn’s sign was predictive of testicular torsion, whereas fever, dysuria, high leucocyte counts in blood and/or urine, high blood C-reactive protein, and burning pain were predictive of genital/paragenital infection. Color Doppler ultrasound did not help to distinguish between torsion and infection.Testicular Doppler-Sonography. Doppler ultrasound of the testis can detect a lack of blood flow in the testis with 90% sensitivity and 99% specificity, 1% false positive results. Some studies found worse results. If the patient presents with typical signs and symptoms of testicular torsion, the detection of a testicular blood flow should be questioned. Loss of the cremasteric reflex is associated with testicular torsion, but always consider the clinical picture (plus any Doppler imaging) in addition to this clinical sign. Prehn’s Sign. Prehn’s Sign can be used to help differentiate . Torsion of the testicular appendages is considered the most common cause of acute scrotal pain in prepubertal children and may even be the single most prevalent cause of pediatric orchalgia.[1] Therefore, it should be included in the differential diagnosis for any male presenting with an acute scrotum, particularly in the pediatric age group.[1] Two testicular .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of .Testicular torsion must be considered in any patient who complains of acute scrotal pain and swelling. . a thorough physical examination and appropriate diagnostic tests. The onset, character .Scrotal and testicular masses can be broadly categorized into painful conditions, which include testicular torsion, torsion of the testicular appendage, and epididymitis, and painless conditions .Prehn’s test: if testicular pain is relieved by elevating the testes, suspect epididymitis; if not, suspect testicular torsion; Cremasteric reflex: stroke inside of leg and watch scrotal skin tighten (usually absent in torsion) Testicular pathology Finally .
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility. . A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard Diagnostic Test Study. J Urol .Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .
The transillumination test is negative. Doppler ultrasound shows absent blood flow in the right testis, consistent with testicular torsion. . A patient presenting with testicular torsion will have a negative prehn’s sign (lifting of testicle will not relieve pain). A positive prehn's sign is seen in patients with epididymitis, they will .Testicular torsion typically presents with an acute, sudden onset of scrotal pain, often associated with nausea (PPV 96%, sensitivity of 69%) and vomiting (PPV 98%, sensitivity 60%). . Negative Prehn’s sign – historically used to differentiate torsion from epididymitis where scrotal elevation would provide relief of pain in epididymitis .
In testicular torsion, unlike in orchitis or epididymitis, elevating the scrotum to take pressure off the testes usually does not ease the pain—this is known as a negative Prehn’s sign. 1,2,13 A history of the pain easing gradually may not be a good sign, as this is an indicator of testicular necrosis. 10Prehn's Sign and Cremasteric Reflex are unreliable and should not be used alone to rule-out Testicular Torsion. No single exam finding either rules-in or rules-out Testicular Torsion; Pain may have improved or resolved at presentation despite persistent Testicular Torsion. Nerve becomes ischemic on twisting with vascular supply
testicular torsion management pdf
testicular torsion in adults
thickness measurement painting
testicular torsion hydrocele
Resultados de lotería de Frutas: Revisa los resultados de los .
prehn's test in testicular torsion|testicular torsion after surgery